This article is the continuation of the Series on the C programming tutorial and carries the discussion on C language programming and its implementation. In our last tutorial, we discussed the Little Endian and Big Endian in C programming. In this article, we are going to see flow control in C or control statements in C programming. It aims to provide easy and practical examples for understanding the C program.
Table of Contents
Flow Control in C
What is flow control?
We can understand the flow control using the below example.
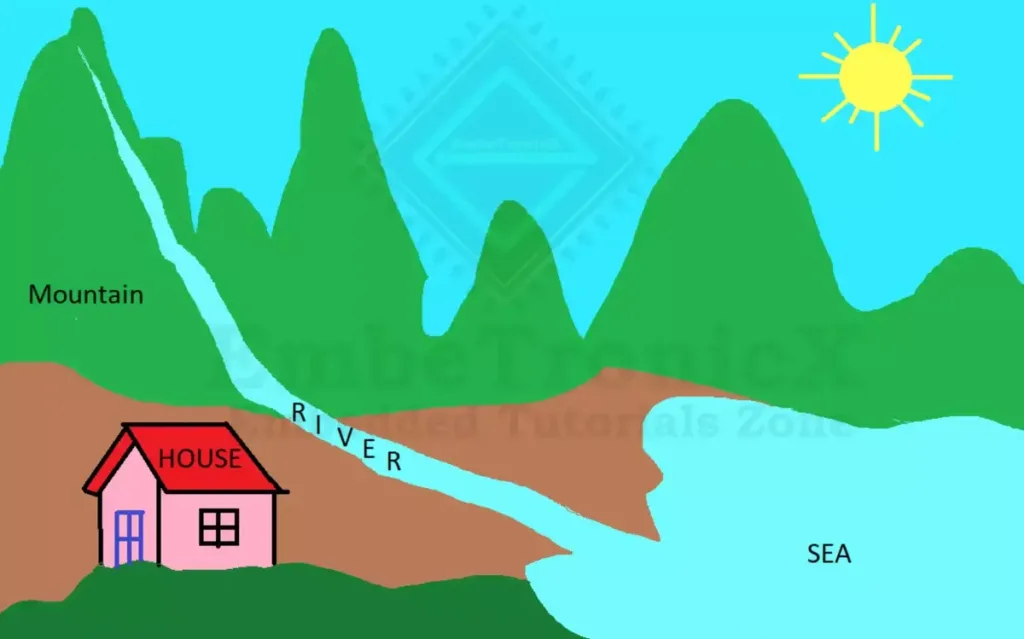
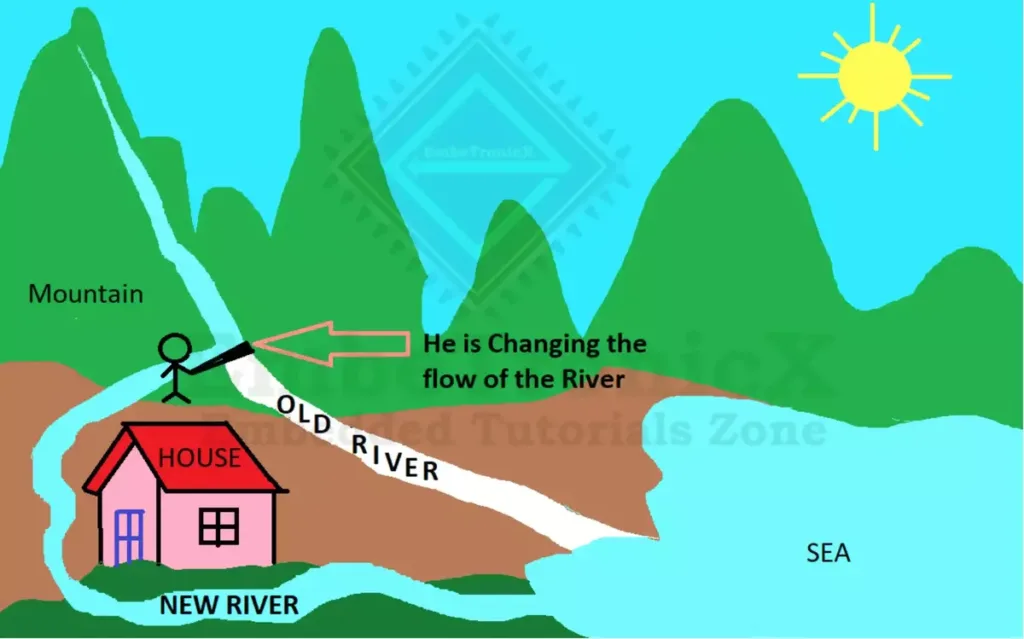
In real life, we will take the river as an example. See the below image. The river flows from the mountain to the sea directly. (Sorry for my bad drawing).
Now the farmer wants to change the path or flow of the river. He is filling something in the river. So, the path of the river flow is changing. See the below image for an understanding.
So, Like he changes the flow of the river, there are many examples available in real life.
|
|
|
What is Flow control in C?
Flow control refers to the execution order of statements or instructions in a program. It allows developers or programmers to control the flow and sequence of code execution based on certain conditions or criteria. Flow control statements are used to make decisions, repeat blocks of code, and jump to specific sections of code.
There are several types of flow control statements commonly used in C programming:
-
Conditional Statements: These statements allow the program to make decisions based on a condition. The most commonly used conditional statements are:
- if statement: Executes a block of code if a certain condition is true.
- if-else statement: Executes one block of code if a condition is true and another block if the condition is false.
- else-if statement: Executes one block of code if a condition is true and another block if the other condition is true.
- nested-if statement: It has if statements inside the another if statement.
- switch statement: Allows for multiple branches of execution based on different values.
-
Looping Statements: Looping statements allow a block of code to be repeated multiple times. The most commonly used looping statements are:
- for loop: Executes a block of code for a fixed number of iterations.
- while loop: Repeats a block of code as long as a certain condition is true.
- do-while loop: Repeats a block of code at least once, and then continues repeating as long as a certain condition is true.
-
Control Transfer Statements: These statements change the normal flow of execution within a program. These statements are also called as Jumping statements.
- break statement: Terminates the execution of a loop or switch statement.
- continue statement: Skips the current iteration of a loop and continues with the next iteration.
- goto statement: It transfers the control from one part of the code to another labeled part.
- return statement: Ends the execution of a function and returns a value to the caller.
Flow control statements provide a way to make programs more dynamic and adaptable by allowing different paths of code execution based on specific conditions or requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q) What is control flow in c?
Flow control in C refers to the management of the execution order of statements within a C program. It allows the programmer to control the flow of program execution based on various conditions. Flow control is essential in C as it helps in making decisions, performing repetitive tasks, and handling different situations within the program. There are several flow control structures in C, such as if-else, switch case, loops (for, while, do-while), and break and continue statements. These structures enable the programmer to write structured and organized code, leading to efficient program execution.
Q) Why do we need flow control in C programming?
Flow control is essential in C programming as it allows the sequential execution of instructions, control loop iterations, and conditional branching. Without flow control, programs would execute in a linear and predictable manner without the ability to make decisions or repeat sections of code. Flow control constructs such as if-else statements, loops, and switches provide flexibility and allow programmers to create dynamic and interactive programs.
In our next tutorial, we will discuss the if statements in C programming.
You can also read the below tutorials.
|
|
|

Embedded Software | Firmware | Linux Devic Deriver | RTOS
Hi, I am a tech blogger and an Embedded Engineer. I am always eager to learn and explore tech-related concepts. And also, I wanted to share my knowledge with everyone in a more straightforward way with easy practical examples. I strongly believe that learning by doing is more powerful than just learning by reading. I love to do experiments. If you want to help or support me on my journey, consider sharing my articles, or Buy me a Coffee! Thank you for reading my blog! Happy learning!