This article is the continuation of the Series on the C programming tutorial and carries the discussion on C language programming and its implementation. It aims to provide easy and practical examples for understanding the C program. In our last article, we have seen the Enum in C programming. In this tutorial, we are going to see Typecasting in C programming language. Let’s begin.
You can also read pointers in c, embedded interview topics, and bitwise operators in c.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Typecasting is a way to convert a variable from one data type to another data type. For example, if you want to store a long value into a simple integer then you can type cast long to int. You can convert values from one type to another explicitly using the cast operator.
The new data type should be mentioned before the variable name or value in brackets which to be typecast.
Typecasting example program
In the below C program, 7/5 alone will produce an integer value of 1. So, typecast is done before division to retain float value (1.4).
|
|
|
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
float x;
x = (float) 7/5;
printf(“value = %f”,x);
}
Output:
value = 1.400000
What is typecasting in C Language?
Converting an expression of a given type into another type is known as typecasting. typecasting is more used in C language programming.
Here, It is best practice to convert the lower data type to the higher data type to avoid data loss.
Data will be truncated when the higher data type is converted to the lower. For example, if the float is converted to int, data that is present after the decimal point will be lost.
There are two types of type casting in c language.
|
|
|
Types of typecasting in C
- Implicit Conversion
- Explicit Conversion
Implicit conversion
Implicit conversions do not require any operator for conversion. They are automatically performed when a value is copied to a compatible type in the program. Here, the value of a has been promoted from int to double and we have not had to specify any typecasting operator. This is known as a standard conversion.
Example:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=20;
double p;
p=i; // implicit conversion
printf(“implicit value is %d”,p);
}
Output:-
implicit value is 20
Explicit conversion
In C language, Many conversions, especially those that imply a different interpretation of the value, require an explicit conversion. We have already seen two notations for explicit type conversion. They are not automatically performed when a value is copied to a compatible type in the program.
Example:-
|
|
|
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=20;
short p;
p = (short) i; // Explicit conversion
printf(“Explicit value is %d”,p);
}
Output:-
Explicit value is 20
Usual Arithmetic Conversion
The usual arithmetic conversions are implicitly performed to cast their values in a common type, C uses the rule that in all expressions except assignments, any implicit type conversions made from a lower size type to a higher size type as shown below:
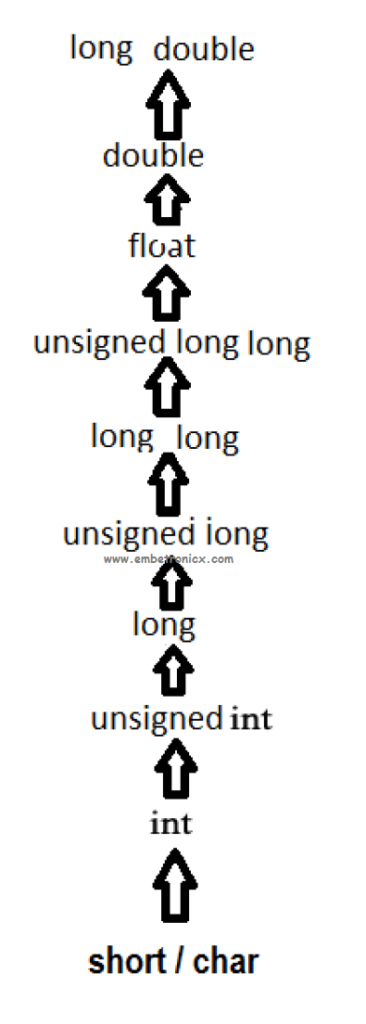
Inbuilt Typecast Functions In C
There are many inbuilt typecasting functions available in C language that perform data type conversion from one type to another.
| S.No | TypeCast Function | Description |
| 1 | atof() | Convert string to Float |
| 2 | atoi() | Convert string to int |
| 3 | atol() | Convert string to long |
| 4 | itoa() | Convert int to string |
| 5 | ltoa() | Convert long to string |
Things to remember when you typecast in C program
When it comes to typecasting in a C program, there are a few important things to keep in mind:
- Understand the purpose: Typecasting allows you to convert a variable from one data type to another. It can be useful when you want to perform certain operations that require matching data types.
- Use the correct syntax: To perform a typecast, enclose the variable or expression you want to convert within parentheses and precede it with the desired data type. For example:
(float)num. - Be aware of data loss: Typecasting can result in data loss if you convert a variable into a smaller data type. For instance, if you convert a
floatto anint, the fractional part will be truncated. - Beware of undefined behavior: Typecasting pointers between different types should be done with caution. Improper use of typecasting pointers can lead to undefined behavior or memory access violations.
- Be mindful of compatibility: Ensure that the types you’re casting between are compatible. Typecasting may not always result in meaningful conversions, especially if the types are not compatible.
- Handle potential errors: It’s a good practice to check the range and validity of values before typecasting. This helps avoid potential errors or unexpected results.
- Maintain code readability: While typecasting can be useful, excessive or unnecessary typecasting can make the code difficult to read and understand. Use typecasting judiciously and consider alternative approaches if possible.
Remember, typecasting should be used sparingly and only when necessary. It is important to understand the implications and potential risks associated with typecasting in order to write reliable and maintainable C programs.
|
|
|
In our next article, we will see Qualifiers in C programming.
You can also read the below tutorials.

Embedded Software | Firmware | Linux Devic Deriver | RTOS
Hi, I am a tech blogger and an Embedded Engineer. I am always eager to learn and explore tech-related concepts. And also, I wanted to share my knowledge with everyone in a more straightforward way with easy practical examples. I strongly believe that learning by doing is more powerful than just learning by reading. I love to do experiments. If you want to help or support me on my journey, consider sharing my articles, or Buy me a Coffee! Thank you for reading my blog! Happy learning!


