Recently, we have received the STM32 Nucleo-144 board. We wanted to explore the Zephyr RTOS using the STM32 Nucleo board. We will be providing the Zephyr RTOS tutorials using this Zephyr RTOS Tutorial Series. This post will help you to setup Zephyr RTOS for STM32 Nucleo (Getting Started Zephyr RTOS) and we will run the basic Blinky program.
You can also read the FreeRTOS Tutorials, STM32 CMSIS RTOS Getting started, Boot sequence in Cortex-M4, STM32 Bootloader tutorials, and NuttX RTOS Tutorials.
Table of Contents
Setup Zephyr RTOS for STM32 Nucleo
Prerequisites
If you want to know about the RTOS and how it is working, then please read the below posts first.
Hardware Required
We have our own EmbeTronicX Store called ChipTronicX. You can purchase the hardware from ChipTronicX.
- STM32F767Zi Nucleo (You can use any STM32 boards).
- LED (If you don’t have onboard LED)
- Ubuntu machine or Windows machine with VirtualBox
Introduction
Whenever people talk about RTOS, mostly they used to talk about FreeRTOS, uCOS, Keil RTX, RT Linux, VxWorks, etc. In recent days, we have been hearing about the NuttX RTOS and Zephyr RTOS here and there. We have posted the NuttX RTOS already. Now we will see the Zephyr RTOS.
|
|
|
What is Zephyr RTOS?
The Zephyr Project, is an open-source RTOS, by the Linux Foundation. It is a scalable real-time operating system (RTOS) supporting multiple hardware architectures, optimized for resource-constrained devices, and built with security in mind.
As a Linux Foundation-hosted collaborative effort, the Zephyr ProjectTM unites leaders from across the tech industry in pursuit of the improvement of IoT device performance and interoperability.
The Zephyr OS is based on a small-footprint kernel designed for use on resource-constrained systems: from simple embedded environmental sensors and LED wearables to sophisticated smart watches and IoT wireless gateways.
The Zephyr kernel supports multiple architectures, including ARM Cortex-M, Intel x86, ARC, Nios II, Tensilica Xtensa, and RISC-V, and a large number of supported boards.
|
|
|
We can expect common kernel features like threads, semaphores, etc. than other RTOSes provide. Zephyr RTOS might become the first open-source, safety-certified RTOS ever.
Key features of Zephyr RTOS
As more and more vendors bring new IoT systems to market, consumers will start finding it difficult to connect (and use) all different devices together. A scalable, open platform like Zephyr mitigates this problem by making it easier for developers to build interoperable IoT applications across a range of device types. This means that, for example, your thermostat will be able to communicate with your security camera, which will be able to communicate with your smart home hub, which will be able to communicate with your smartphone.
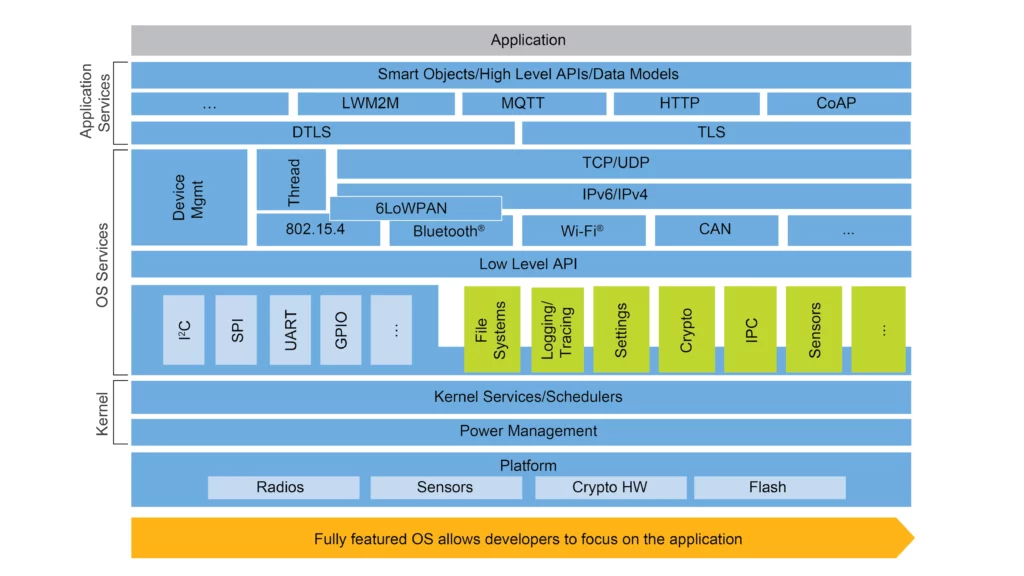 [Image source – NXP]
[Image source – NXP]
- Open-source real-time operating system
- Extensive suite of Kernel services
- Multiple Scheduling Algorithms
- Highly configurable / Modular for flexibility
- Cross Architecture
- Memory Protection
- Compile-time resource definition
- Optimized Device Driver Model
- Devicetree Support
- Bluetooth Low Energy 5.0 support
- Native Linux, macOS, and Windows Development
- Virtual File System Interface with LittleFS and FATFS Support
- Product development ready
- Includes security updates
You can read the complete details here.
If you want to contribute to the Zephyr RTOS, you can check this page.
|
|
|
Setup Zephyr RTOS for STM32
Zephyr has excellent documentation and a complete System Development Kit (SDK). You can always refer to the official documentation page if you need any clarification.
You can also go through the video explanation.
In this tutorial series, we will be using the ubuntu machine as a host machine. If you don’t have the Ubuntu machine, then install the VirtualBox in your windows machine and install the Ubuntu OS. You can check out the official page for Windows setup if you don’t want to use Ubuntu. Let’s get started.
Update the system
Open up a terminal window and issue the below command.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade |
Install dependencies
Download, inspect and execute the Kitware archive script to add the Kitware APT repository to your sources list.
|
|
|
wget https://apt.kitware.com/kitware-archive.sh sudo bash kitware-archive.sh |
Then install the required applications using the below command.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends git cmake ninja-build gperf ccache dfu-util device-tree-compiler wget python3-dev python3-pip python3-setuptools python3-tk python3-wheel xz-utils file make gcc gcc-multilib g++-multilib libsdl2-dev |
Get Zephyr and install Python dependencies
As of now, we should have installed the CMake, python, and Devicetree compiler.
Now we will install the westand add that to the environment variable using the below commands.
pip3 install --user -U west echo 'export PATH=~/.local/bin:"$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc |
Let’s get the Zephyr source code using the west. Run the below commands.
west init ~/zephyrproject cd ~/zephyrproject west update west zephyr-export |
Now, we will install Zephyr’s additional python requirements by running Zephyr’s scripts/requirements.txt.
|
|
|
pip3 install --user -r ~/zephyrproject/zephyr/scripts/requirements.txt |
Install a Toolchain
A toolchain provides a compiler, assembler, linker, and other programs required to build Zephyr applications.
Download the latest SDK installer using the below command.
cd ~ wget https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/sdk-ng/releases/download/v0.13.2/zephyr-sdk-0.13.2-linux-x86_64-setup.run |
Run the installer using the below commands.
chmod +x zephyr-sdk-0.13.2-linux-x86_64-setup.run ./zephyr-sdk-0.13.2-linux-x86_64-setup.run -- -d ~/zephyr-sdk-0.13.2 |
Now, you should have the new directory called ~/zephyr-sdk-0.13.2.
Finally, we will install the udev rules and configure them.
|
|
|
sudo cp ~/zephyr-sdk-0.13.2/sysroots/x86_64-pokysdk-linux/usr/share/openocd/contrib/60-openocd.rules /etc/udev/rules.d sudo udevadm control --reload |
We are all set. Let’s build the Blinky source code.
Build Sample Blinky Program
Let’s go to the source code directory. Then we can build the source code by using the below command.
cd ~/zephyrproject/zephyr west build -p auto -b <your-board-name> samples/basic/blinky |
In the above command, you can replace the <your-board-name> to your development board. For example, We are using the STM32F767Zi Nucleo board. So, we will replace the <your-board-name> to nucleo_f767zi. Refer to the below command.
west build -p auto -b nucleo_f767zi samples/basic/blinky |
Flash the Blinky
Before you flash the code, connect the STM32 Nucleo board to the machine. Then run the below command.
west flash |
Now, check the LED. It should blink in a 1-second interval.
|
|
|
Video Explanation and Output
[Will be added soon]
You can also read the below tutorials.
Reference(s):

Embedded Software | Firmware | Linux Devic Deriver | RTOS
Hi, I am a tech blogger and an Embedded Engineer. I am always eager to learn and explore tech-related concepts. And also, I wanted to share my knowledge with everyone in a more straightforward way with easy practical examples. I strongly believe that learning by doing is more powerful than just learning by reading. I love to do experiments. If you want to help or support me on my journey, consider sharing my articles, or Buy me a Coffee! Thank you for reading my blog! Happy learning!



